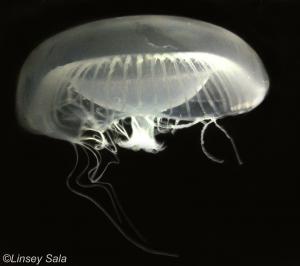
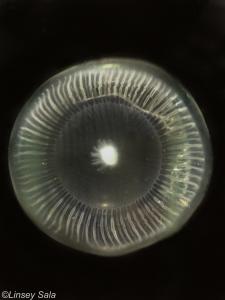
Aequorea spp.
Distribution:
Bering Sea to Baja California, also in the Gulf of California.
Habitat:
Nearshore coastal areas and large bays.
Size:
80-250 mm bell diameter, as adults.
Diet:
Primarily softbodied prey such as other jellies, ctenophores, and appendicularians
Predators:
Other jellyfish and hydromedusae; can be cannibalistic.
Useful Facts or Characters:
Clear with many long, fine tentacles; bioluminescent around bell margin.
Natural History:
Commonly called crystal jellies, they are raised in many aquaria. Generally present during the spring or early autumn. Large blooms occur in British Columbia, but blooms are not common in southern California. The polyp stage is rarely found in the field.
References:
Torrey, H.B. (1909) The Leptomedusae of the San Diego Region. University of California Publications in Zoology 6: 11-31.
Wrobel, D., and Mills, C. (1998) Pacific Coast pelagic invertebrates: a guide to the common gelatinous animals. Sea Challengers, Monterey Bay Aquarium, Monterey, CA.