Species by Order: Thecosomata
| Natural History | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
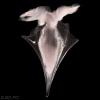
Cavolinia inflexa |
Cavolinia form mucus feeding webs and ingest these webs with their captured prey. Each of these processes can take between 1-3 minutes. |
 |
Clio pyramidata |
Known to be an intermediate host for parasitic copepods that eventually infest fish. Several forms exist within the California Current, but here no attempt was made to distinguish them. |
 |
Corolla spectabilis |
Mucous feeding web can be up to 2 meters in diameter. |
 |
Creseis virgula |
An escape response is to drop the mucus feeding web and sink with the shell pointed vertically. Several forms reported; here no attempt is made to distinguish them. |
 |
Desmopterus pacificus |
Desmopterus papilio is a closely related species in the Pacific, but has longer tentacles than Desmopterus pacificus. |
 |
Heliconoides inflatus |
Fed upon by the gymnosome Clione limacina, which places the opening of the thecosome Limacina shell up to its mouth and uses hooks to pull out the soft tissue. |
 |
Limacina helicina |
As in many shell-bearing pteropods, the aragonitic shell is sensitive to changes in ocean pH. |
